Nucleotides (IMP, GMP)
2020.03.17

Nucleotides are not classifed as an essential nutrients because they can be synthesized using proteins and carbohydrates
in the body. However, when cell division happens at fast rate, external intake is essential (e.g. rapid growth, especially
during infancy, and stress relief).
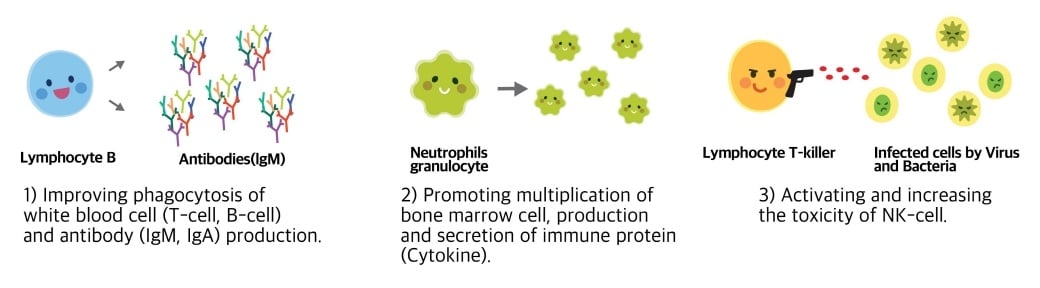
Effects of nucleotide on immunity
Improving Immune System
Bio-synthesis of nucleotide is impossible in immune cells such as white blood cell, red blood cell, bone marrow cell, intestinal cell and lymphocyte (Sanderson and He, 1994). That means, nucleotides can be supplied only through salvage synthetic pathway (exogenous).\
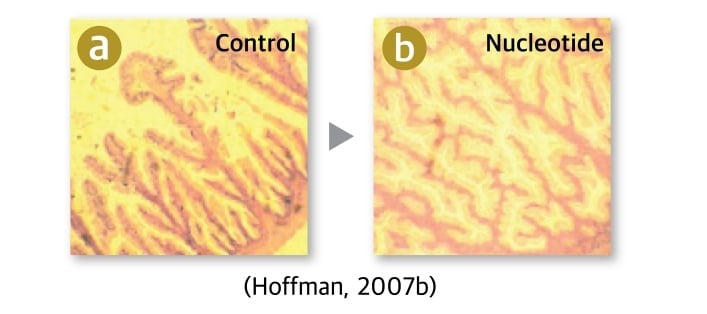
Improving Gut Health
1) Nucleotides promote intestinal damage recovery after diarrhea.
2) Nucleotides increase the growth of Bifidobacteria in intestine (pH↓, as pre-biotics).
3) Nucleotides increase beneficial bacteria (Lactobacillus ↑ ) and decreases harmful bacteria (E. coli↓ ).
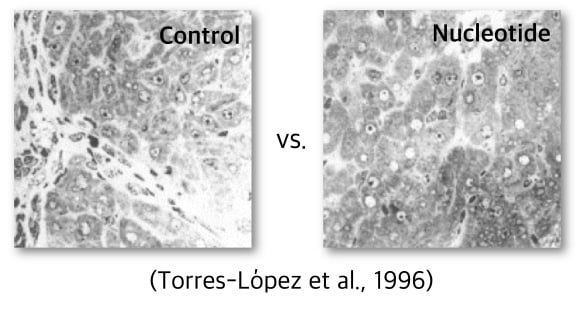
Improving Liver Function
Liver is a major organ that regulates nucleotides content in the body by
synthesis and release of nucleotides for body homeostasis.
1) Nucleotides regulate hepatocyte growth and regeneration.
2) Nucleotide requirements are increased (Salvage and/or bio-synthesis)
after liver injury.
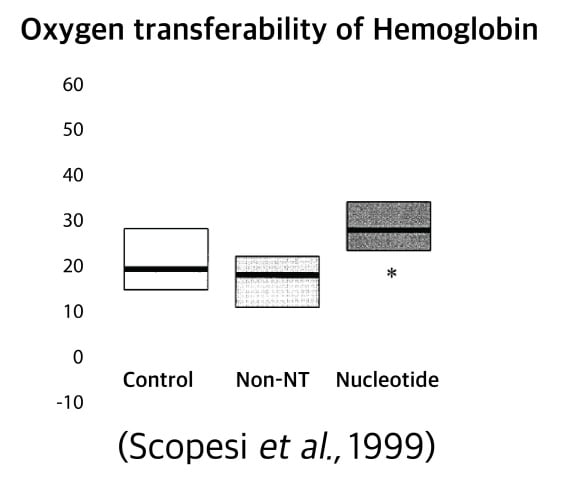
Improving Stress Tolerance
De novo synthetic ability of nucleotides in Hematopoietic stem cell and marrow cell is limited.
1) Nucleotides support hematopoiesis and increase affinity of RBC (Yamamoto et al., 1997).
2) Nucleotides enhance the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin and increases oxygen transport (Scopesi et al., 1999).
*References are available on request























